Koha/Anwender: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| (157 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
[[image:Koha_anwender02_20180714.png|thumb|right|400px| | [[image:Koha_anwender02_20180714.png|thumb|right|400px|Fast 5'100 im Bibliotheksverzeichnis libraries.org eingetragene Koha-Anwender weltweit (Mai 2019)<!-- - <span class="plainlink">[http://librarytechnology.org/map.pl?ILS=Koha aktuelle Karte]</span> -->]] | ||
Die Zahl der <b>Anwender</b> des Bibliothekssystems [[Koha]] wird | Die Zahl der <b>Anwender</b> des Bibliothekssystems [[Koha]] wird auf rund 15'000 Bibliotheken geschätzt. Zu den einsetzenden Bibliotheken gehören solche aller Grössen und Typen - Nationalbibliotheken, öffentliche und wissenschaftliche Bibliotheken sowie Schul-, Firmen- und Spezialbibliotheken. | ||
Viele Anwender von Koha haben sich zu regionalen, nationalen oder sprachabhängigen [[Koha-Anwendergruppen]] zusammengeschlossen. | Viele Anwender von Koha haben sich zu regionalen, nationalen oder sprachabhängigen [[Koha-Anwendergruppen]] zusammengeschlossen. | ||
| Zeile 10: | Zeile 10: | ||
Zur Zahl der tatsächlichen Koha-Anwender gibt es naturgemäss keine genauen Zahlen, da jeder Beliebige die Software herunterladen und installieren kann, ohne jemanden davon zu benachrichtigen oder dafür bezahlen zu müssen. | Zur Zahl der tatsächlichen Koha-Anwender gibt es naturgemäss keine genauen Zahlen, da jeder Beliebige die Software herunterladen und installieren kann, ohne jemanden davon zu benachrichtigen oder dafür bezahlen zu müssen. | ||
Die Firma Catalyst IT sowie der Bibliothekswissenschaftler Marshall Breeding aus den USA schätzten die Zahl der weltweiten Koha-Installation im August 2016 auf | Die Firma Catalyst IT sowie der Bibliothekswissenschaftler Marshall Breeding aus den USA schätzten die Zahl der weltweiten Koha-Installation im August 2016 auf rund <span class="plainlinks">[https://lists.katipo.co.nz/public/koha/2016-August/046089.html 15'000]</span>. Breeding geht davon aus, dass Koha das weltweit am meisten eingesetzte Bibliothekssystem überhaupt ist. In seinem Bibliotheksverzeichnis <span class="plainlink">[http://www.librarytechnology.org/libraries/ libraries.org]</span> haben sich davon gegenwärtig 5'989 Bibliotheken freiwillig eingetragen, davon 2'139 aus den USA, 965 aus der Türkei, 472 aus Grossbritannien, 311 aus Frankreich, 70 aus Deutschland, 23 aus der Schweiz und 14 aus Österreich (Stand: 28. Mai 2024). | ||
Galen Charlton beschrieb in seinem Artikel <span class="plainlinks">[https://galencharlton.com/blog/2016/08/visualizing-the-global-distribution-of-koha-installations-from-debian-packages/ Visualizing the global distribution of Koha installations from Debian packages]</span> (August 2016) ein Python-Skript mit dem er die ungefähre geografische Verteilung der Downloads der Koha-Debian-Pakets sichtbar machte. Für die so entstandene Weltkarte verarbeitete er Daten von über 25'000 vollständigen Downloads des Pakets "koha-common" von 9'432 IP-Adressen. Natürlich entspricht nicht jeder Download automatisch einer produktiven Installation. Umgekehrt kommt es aber sicher auch vor, dass zentrale Stellen das Paket nur einmal herunterladen und dann an sehr viel Institutionen verteilen - so gibt es beispielsweise in der Türkei über | Galen Charlton beschrieb in seinem Artikel <span class="plainlinks">[https://galencharlton.com/blog/2016/08/visualizing-the-global-distribution-of-koha-installations-from-debian-packages/ Visualizing the global distribution of Koha installations from Debian packages]</span> (August 2016) ein Python-Skript mit dem er die ungefähre geografische Verteilung der Downloads der Koha-Debian-Pakets sichtbar machte. Für die so entstandene Weltkarte verarbeitete er Daten von über 25'000 vollständigen Downloads des Pakets "koha-common" von 9'432 IP-Adressen. Natürlich entspricht nicht jeder Download automatisch einer produktiven Installation. Umgekehrt kommt es aber sicher auch vor, dass zentrale Stellen das Paket nur einmal herunterladen und dann an sehr viel Institutionen verteilen - so gibt es beispielsweise in der Türkei über 900 Bibliotheken mit Koha und dennoch vergleichsweise wenige auf der Karte sichtbare Downloads, womöglich weil die Verteilung dort über das nationale Ministerium für Kultur und Tourismus erfolgt. | ||
<!-- 2009 etwa 800 Bibliotheken im Verzeichnis lib-web-act | <!-- 2009 etwa 800 Bibliotheken im Verzeichnis lib-web-act | ||
| Zeile 24: | Zeile 24: | ||
* 2018.07.14: 4'927 | * 2018.07.14: 4'927 | ||
* 2018.11.28: 5'002 | * 2018.11.28: 5'002 | ||
* 2019.05.29: 5'095 | |||
* 2019.12.02: 5'151 | |||
* 2020.06.01: 5'014 | |||
* 2020.11.29: 5'169 | |||
* 2021.05.28: 5'131 | |||
* 2021.11.26: 5'189 | |||
* 2022.05.28: 5'279 | |||
--> | --> | ||
== Koha-Anwender im deutschsprachigen Raum == | == Koha-Anwender im deutschsprachigen Raum == | ||
Für den deutschsprachigen Raum (Deutschland, Österreich, Schweiz) | Für den deutschsprachigen Raum (Deutschland, Österreich, Schweiz) strebte ich bis Ende 2022 eine vollständige Auflistung an. Seitdem führe ich hier zusätzlich nur noch die durch die Admin Kuhn GmbH migrierten oder betreuten Koha-Anwender auf. | ||
<!-- | |||
Die übrigen Angaben (Links, Bemerkungen) sind aber jeweils nur so aktuell wie die letzten Nachrichten zur einzelnen Bibliothek. | |||
<b>[[Spezial:Kontakt|Bitte teilen Sie mir doch Ihnen bekannte weitere Koha-Bibliotheken mit!]]</b> | <b>[[Spezial:Kontakt|Bitte teilen Sie mir doch Ihnen bekannte weitere Koha-Bibliotheken mit!]]</b> | ||
--> | |||
=== Deutschland === | === Deutschland === | ||
<!-- In Deutschland wird Koha seit Oktober 2009 vom Bibliotheksservice-Zentrum Baden-Württemberg als Software-as-a-Service angeboten. --> | <!-- In Deutschland wird Koha seit Oktober 2009 vom Bibliotheksservice-Zentrum Baden-Württemberg als Software-as-a-Service angeboten. --> | ||
<!-- Weitere Koha-Anwender ohne genaue Angaben: | |||
* libraries of the Berlin astronomical observatories, André Hartmann | |||
--> | |||
<!-- VORLAGE --> | |||
<!-- | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[ ]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Dezember 2021 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | {| class=wiki width=100% | ||
! width=10% | Ort | ! width=10% | Ort | ||
! width=45% | Bibliothek | ! width=45% | Bibliothek | ||
! width=5% | OPAC | ! width=5% | OPAC | ||
! width=40% | | ! width=40% | Migriert und/oder unterstützt durch Admin Kuhn GmbH | ||
|- | |||
| Aachen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.fir.rwth-aachen.de/ Forschungsinstitut für Rationalisierung e. V. an der RWTH Aachen]</span> | |||
| nur intern | |||
| | |||
* seit April 2021 | |||
* 62'700 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Allegro zu Koha 21.05 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Forschungsinstituts für Rationalisierung e. V. an der RWTH Aachen mit Koha 19.11 bzw. Koha 21.05|Produktionsbeginn des Forschungsinstituts für Rationalisierung e. V. an der RWTH Aachen mit Koha 19.11 bzw. Koha 21.05]] | |||
|- | |||
| Achern | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.achern.de/de/Leben-Lernen/Stadtbibliothek Stadtbibliothek Achern]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-achern.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit August 2021 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Ahlen | | Ahlen | ||
| Zeile 56: | Zeile 98: | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Altenberg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bibliothek-altenberg.de/ Stadt- und Schulbibliothek Altenberg]</span> | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-altenberg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit | * seit August 2022 | ||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Altenburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://landesarchiv.thueringen.de/altenburg/ Landesarchiv Thüringen - Staatsarchiv Altenburg]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://tsaabg.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Altenburg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.lindenau-museum.de/ Lindeau-Museum Altenburg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://lma.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützung durch ThuLB Jena | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Apenrade | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.buecherei.dk/index.php/de/ Deutsche Büchereien Nordschleswig]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | * Zentralbibliothek Apenrade mit den Büchereien Hadersleben, Sonderburg, Tondern und Tingleff | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://zb-apenrade.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| Augsburg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://stadtbuecherei.augsburg.de/ Stadtbücherei Ausgburg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-augsburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit August 2021 | ||
* | * Wechsel von SISIS-Sunrise zu Koha | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bad Honnef | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.iubh.de/ Internationale Hochschule Bad Honnef - Bonn / IUBH]</span> | ||
| | | nur intern | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Oktober 2016 | ||
* Mirko Tietgen | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bad Pyrmont | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.badpyrmont.de/erleben-und-geniessen/events-kulturveranstaltungen/stadtbibliothek/ Stadtbibliothek Bad Pyrmont]</span> | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-badpyrmont.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt | * seit Mai 2020 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Baden-Baden | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.baden-baden.de/stadtbibliothek/ Stadtbibliothek Baden-Baden]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-badenbaden.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* seit | <!-- | ||
* seit Juni 2021 | |||
* Migration von | * Migration von BiBer/Axiell zu Koha | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bayreuth | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.rwg-bayreuth.de/ Richard-Wagner-Gymnasium Bayreuth]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://koha.rwg-bayreuth.de:88/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |||
| <b>Verbund</b> | |||
| Verbund Beckum/Neubeckum | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[https://www.beckum.de/de/bildung/buechereien/oeffentliche-buecherei-beckum.html Öffentliche Bücherei Beckum]</span> | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[https://www.beckum.de/de/bildung/buechereien/stadtbuecherei-neubeckum.html Stadtbücherei Neubeckum]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://vb-beckum.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Februar 2019 | ||
* vorher beide mit Bibliotheca | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |||
| Bergneustadt | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.wiedenest.de/ Forum Wiedenest e. V.]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bib.wiedenest.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit September 2023 | |||
* 55'500 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Bibdia zu Koha 22.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Forum Wiedenest e. V. mit Koha 22.11|Produktionsbeginn des Forum Wiedenest e. V. mit Koha 22.11]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Berlin | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.apabiz.de/ Antifaschistisches Pressearchiv und Bildungszentrum Berlin e. V.]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://bibliothek.apabiz.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Seit | * Seit 2013 | ||
* | * 15'000 Medien und 900 Zeitschriftentitel | ||
* Migration durch Matthias Mann | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Berlin | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothekderfreien.de/ Bibliothek der Freien]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://katalog.bibliothekderfreien.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |||
|- | |||
| Berlin | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://bbf.dipf.de/ Bibliothek für Bildungsgeschichtliche Forschung / BBF des Deutschen Instituts für Internationale Pädagogische Forschung]</span> | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothekskatalog.bbf.dipf.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Unterstützt vom BSZ | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.berlin.bard.edu/ ECLA of Bard, a Liberal Arts University in Berlin]</span> | ||
| | | nur intern | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * wohl https://berlin.bard.edu/academics/academic-services/library/ | ||
* Unterstützt | * Unterstützt durch PTFS Europe | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://eoto-archiv.de/ Each One Teach One (EOTO) e. V.]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://kosboth.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* seit März 2018 | |||
* | * 5'100 Titeldatensätze | ||
* Migration von MS Excel zu Koha 17.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der EOTO Bibliothek mit Koha 17.11|Produktionsbeginn der EOTO Bibliothek mit Koha 17.11]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ernst-abbe.de/ Ernst-Abbe-Gymnasium]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://eas.b-nk-eagy.logoip.de:5080/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.diakonie.de/das-evangelische-werk-fuer-diakonie-und-entwicklung Evangelisches Werk für Diakonie und Entwicklung e. V. / EWDE]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek.ewde.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* seit August 2023 | |||
* 96'800 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha 22.05 | |||
* <!-- [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Evangelischen Werks für Diakonie und Entwicklung e. V. mit Koha 22.05|Produktionsbeginn des Evangelischen Werks für Diakonie und Entwicklung e. V. mit Koha 22.05]] --> | |||
|- | |- | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | |- | ||
| Berlin | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://studiengang.beuth-hochschule.de/veranstaltungstechnik/labor-bibliothek/fachbibliothek-theater-und-veranstaltungstechnik/ Fachbibliothek für Theater- und Veranstaltungstechnik]</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
* Seit etwa 2005 | |||
* Im März 2021 verwendet die Bibliothek eine Software der Firma "paidosoft", womöglich namens "Biblino" | |||
* https://www.biblino.de/index.php?id=358 | |||
* https://www.biblino.de/index.php?action=3&searchmode=0&id=358&searchmode=0&autor=&titel=&schlagworte=&stichwort=&medienart=% | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.fhi.mpg.de/265852/library/ Fritz-Haber-Institut der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://fhilibrary.koha.mpg.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | |||
* seit Januar 2021 | |||
* 26'000 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Allegro-C zu Koha 20.05 in Zusammenarbeit mit der Gesellschaft für wissenschaftliche Datenverarbeitung Göttingen | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Fritz-Haber-Instituts der MPG mit Koha 20.05|Produktionsbeginn des Fritz-Haber-Instituts der MPG mit Koha 20.05]] | |||
|- | |||
| Berlin | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.gks-berlin.de/ Gottfried-Keller-Gymnasium]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gks-berlin.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * BSZ | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.berlin-international.de/hochschule/hochschulstruktur/bibliothek/ Hans-Dieter Klingemann Library, Berlin International University of Applied Sciences]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://koha.berlin-international.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit April 2019 | ||
* | * Migration durch (unbekannt) aufgrund früherer Demoinstallation "bauib" bei mir | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ghwk.de/ Haus der Wannsee-Konferenz]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://ghwk-bibliothekskatalog.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit 2017 (oder Anfang 2018) | ||
* auch über Vufind | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://iqtig.org/ Institut für Qualitätssicherung und Transparenz im Gesundheitswesen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://iqtig.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * BSZ | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.mdc-berlin.de/ Max-Delbrück-Centrum für molekulare Medizin Berlin-Buch]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://koha.mdc-berlin.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | |||
* seit Oktober 2019 | |||
* 43'300 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von SISIS-Sunrise V4.4 und Touchpoint V2.1 zu Koha 18.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Max-Delbrück-Centrums für molekulare Medizin Berlin-Buch mit Koha 18.11|Produktionsbeginn des Max-Delbrück-Centrums für molekulare Medizin Berlin-Buch mit Koha 18.11]] | |||
|- | |||
| Berlin | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.pdi-berlin.de/ Paul-Drude-Institut für Festkörperelektronik]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://144.91.92.204/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit November 2019 | |||
* Neueinführung von Koha 19.05 | |||
|- | |||
| Berlin | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.sprachenzentrum.hu-berlin.de/struktur-ansprechpartner-innen/mediothek Sprachenzentrum der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin]</span> | |||
| nur intern | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit 2015 | ||
* 25'000 Medien | |||
* Migration durch Mirko Tietgen | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Berlin | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://wias-berlin.de/ Weierstrass Institute for Applied Analysis and Stochastics / WIAS]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://koha.wias-berlin.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Balingen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.balingen.de/leben-in-balingen/oeffentliche+einrichtungen/mediothek Mediothek Balingen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://mt-balingen.lmscloud.net./ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit November 2022 | ||
* | * Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha | ||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bietigheim-Bissingen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://buecherei.bietigheim-bissingen.de/ Stadtbücherei Bietigheim-Bissingen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-bietigheim-bissingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit | * seit Oktober 2022 | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bischofswerda | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bischofswerda.de/kultur-freizeit-und-tourismus/bibliothek.html Stadtbibliothek Bischofswerda]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-bischofswerda.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit November 2021 | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bochum | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.hs-gesundheit.de/ Hochschule für Gesundheit]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://boss.bsz-bw.de/HGBO/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* OPAC mit Vufind | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | * Unterstützt vom BSZ | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Böblingen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek.boeblingen.de/ Stadtbibliothek Böblingen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb- | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-boeblingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit | * seit Oktober 2021 | ||
* | * Migration von Axiell Bieber zu Koha | ||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bonn | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.bibb.de/ Bundesinstitut für Berufsbildung / BIBB]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://opac.bibb.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * OPAC mit Vufind | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bonn | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.bonn.de/stadtarchiv Stadtarchiv und Stadthistorische Bibliothek Bonn]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://stahb.bonn.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | |||
* seit September 2022 | |||
* 74'900 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Allegro zu Koha 21.11 | |||
|- | |||
| Bordesholm | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bordesholm.de/cms/front_content.php?idcat=131 Gemeindebücherei Bordesholm]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-bordesholm.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt von | * seit Juni 2018 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Borna | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.mediothek-borna.de/ Mediothek Borna]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://borna.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Dezember 2021 | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Brandenburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://bibliothek- | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bibliothek-brandenburg.de/ Fouqué-Bibliothek]</span> | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-brandenburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Februar 2019 | ||
* | * vorher SISIS-Sunrise | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bretzfeld | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.bretzfeld.de/index.php?id=120 Gemeindebücherei Bretzfeld]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-bretzfeld.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Büdingen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadt-buedingen.de/index.php?La=1&NavID=3139.81&fdirect=1&NavID=3139.81 Stadtbücherei Büdingen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-buedingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit November 2019 | ||
* | * Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bürgel | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.museum-zinsspeicher-thalbuergel.de/ Museum Zinsspeicher]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://mzt.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * wohl seit 2020 | ||
* | * ThüLB Jena | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Büsingen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.eunc.edu/de/ European Nazarene College]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://koha.eunc.edu/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch Interleaf Technology | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Burghausen | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.burghausen.de/unsere-stadt/kulturstadt/stadtbibliothek.html Stadtbibliothek Burghausen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-burghausen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit Juni 2019 | |||
* vorher mit Bibliotheca | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Calau | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.calau.de/verzeichnis/visitenkarte.php?mandat=64718 Stadtbibliothek Calau]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-calau.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt | * Seit Mai 2022 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Camburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://camburg-museum.de/ Stadtmuseum Camburg]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://smc.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Deggendorf | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://stadtbibliothek.deggendorf.de/ Stadtbibliothek Deggendorf]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb- | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-deggendorf.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit September 2019 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Dieburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.dieburg.de/index.php/stadtbibliothek-kultur-155 Stadtbibliothek Dieburg]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb- | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-dieburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit | * seit Juni 2021 | ||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Dietzenbach | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.dietzenbach.de/index.php?NavID=1799.952.1 Stadtbücherei Dietzenbach]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-dietzenbach.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* seit April 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Donaueschingen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.donaueschingen.de/bibliothek Stadtbibliothek Donaueschingen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-donaueschingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Dezember 2021 | ||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Donzdorf | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadtbuechereidonzdorf.de/ Stadtbücherei Donzdorf]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-donzdorf.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit | * seit Januar 2022 | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Dresden | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ihd-dresden.de/ Institut für Holztechnologie Dresden / IHD]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | nur intern | ||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Dresden | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.lfa.sachsen.de/ Landesamt für Archäologie Sachsen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://lfasn.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * BSZ | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Dresden | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.denkmalpflege.sachsen.de/633.htm Landesamt für Denkmalpflege Sachsen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | nur intern | ||
| | |||
* seit Februar 2023 | |||
* 88'800 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Allegro zu Koha 20.11 | |||
* OPAC nur intern bzw. über SWB | |||
|- | |||
| Düsseldorf | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://international-library.de/ International English Library Düsseldorf / IELD]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://catalogue.international-library.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Seit | * Seit 2016 | ||
* | * 26'700 Medien | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Duisburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.duisburg.de/microsites/stadtbibliothek/ Stadtbibliothek Duisburg]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-duisburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* Seit April 2021 | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
* Erste "Sektion 1-Bibliothek" mit Koha in Deutschland, über 150 Mitarbeiter | |||
* Zentralbibliothek, 13 Zweigstellen, Bücherbus | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Eckernförde | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://stadtbuecherei-eckernfoerde.de/ Stadtbücherei Eckernförde]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-eckernfoerde.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit Mai 2019 | ||
* Unterstützt | * Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |||
| Eilenburg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.kulturunternehmung.de/bibliothek.php Bibliothek Eilenburg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-eilenburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit Dezember 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Ellerau | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ellerau.de/buecherei Gemeindebücherei Ellerau]</span> | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-ellerau.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* | * seit Februar 2018 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Ennepetal | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.ennepetal.de/bildung-jugend-soziales/stadtbuecherei/ Stadtbücherei Ennepetal]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-ennepetal.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt von | * Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Erftstadt | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadtbuecherei-erftstadt.de/ Stadtbücherei Erftstadt]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb- | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-erftstadt.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* vorher SISIS-Sunrise (OCLC) | |||
* seit September 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Erfurt | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.evangelische-gemeinschaftsschule-erfurt.de/ Evangelische Gemeinschaftsschule Erfurt]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://ege.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Erfurt | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://tlbg.thueringen.de/ Landesamt für Bodenmanagement und Geoinformation]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://tlavg.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
* Unterstützt | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Erkner | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://leibniz-irs.de/forschungsinfrastruktur/bibliothek Leibnitz-Institut für Raumbezogene Sozialforschung]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://opac.leibniz-irs.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | |||
| | | | ||
* seit | * seit Oktober 2021 | ||
* | * 26'700 Titeldatensätze | ||
* Migration von | * Migration von Allegro-C zu Koha 21.05 | ||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Leibniz-Instituts für Raumbezogene Sozialforschung mit Koha 21.05|Produktionsbeginn des Leibniz-Instituts für Raumbezogene Sozialforschung mit Koha 21.05]] | |||
* [ | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Erkrath | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.erkrath.de/stadtbuecherei Stadtbücherei Erkrath]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb- | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-erkrath.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* seit August 2018 | |||
* vorher BIBDIA | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Esslingen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.seminar-esslingen.de/ Staatliches Seminar für Didaktik und Lehrerbildung (Gymnasien)]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://seminar-esslingen.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Falkensee | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadtbibliothek-falkensee.de/ Stadtbibliothek Falkensee]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-falkensee.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* seit Dezember 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Fehmarn | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[http://buecherei.stadtfehmarn.de/ Stadtbücherei Fehmarn]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-fehmarn.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit | * seit Oktober 2021 | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Fellbach | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://stadtbuecherei.fellbach.de/ Stadtbücherei Fellbach]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-fellbach.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Juli 2022 | ||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Feuchtwangen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.saengermuseum.de/ Sängermuseum]</span> | ||
| | | nur intern | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * arbeitet jedenfalls 2020 mit Koha | ||
* Archiv- und Museumsleiter: Alexander Arlt | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Flensburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bz-sh.de/ Büchereizentrale Schleswig-Holstein]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://leb-flensburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt von | * Seit Februar 2017 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Flensburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://stadtbibliothek.flensburg.de/ Stadtbibliothek Flensburg]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-flensburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit April 2019 | ||
* Unterstützt | * Migration von BIBDIA zu Koha | ||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Flintbek | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.flintbek.de/leben-und-wohnen/bildung/gemeindebuecherei.html Gemeindebücherei Flintbek]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb- | | <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-flintbek.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Zeile 564: | Zeile 721: | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Frankfurt am Main | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.dipf.de/ Deutsches Institut für Internationale Pädagogische Forschung / DIPF]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | * <span class="plainlink">[http://bbf.dipf.de/ Bibliothek für Bildungsgeschichtliche Forschung / BBF]</span> | ||
* <span class="plainlink">[http://www.dipf.de/de/wissenschaftliche-infrastrukturen/bibliotheken/ffb Frankfurter Forschungsbibliothek / FFB]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://ffb.dipf.de/ OPAC]</span><br><span class="plainlink">[http://ffb.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit 2015 | ||
* | * Unterstützt vom BSZ | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Freiburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.eh-freiburg.de/ Evangelische Hochschule Freiburg]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://eh-freiburg.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | * Unterstützt vom BSZ | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Fürstenwalde | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://bibliothek.stadt-fuerstenwalde.de/ Stadtbibliothek Fürstenwalde]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-fuerstenwalde.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Juli 2018 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Fürth | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.fuerth.de/DesktopDefault.aspx/tabid-39/287_read-3886/ Volksbücherei Fürth]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://vb-fuerth.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt | * Seit April 2019 | ||
* Migration von SISIS-Sunrise zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Garching | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.eso.org/sci/libraries.html European Southern Observatory / ESO]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://koha. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://eso.koha-ptfs.eu/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit etwa 2010 | ||
* Unterstützt von PTFS Europe | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Garching | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://stadtbuechereigarching.de/ Stadtbücherei Garching]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb- | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-garching.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Mai 2022 | ||
* Migration von SISIS-Sunrise zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <b>Verbund</b> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | Regionalverbund Geesthacht-Schwarzenbek | ||
* <span class="plainlink">[https://www.geesthacht.de/Bildung-br-Kultur/Stadtb%C3%BCcherei Stadtbücherei Geesthacht]</span> | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[http://www.schwarzenbek.de/index.phtml?NavID=1810.122 Stadtbücherei Schwarzenbek]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-geesch.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | <!-- Februar 2019 --> | ||
|- | |||
| Gengenbach | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadt-gengenbach.de/index.php?id=129 Mediathek Gengenbach]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://mt-gengenbach.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt | * Seit April 2021 | ||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Gera | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.gera.de/sixcms/detail.php?id=10213 Spezialbibliotheken der Stadt Gera]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://bibg.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* | * ThüLB Jena | ||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Gerlingen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.gerlingen.de/Unsere+Buecherei Stadtbücherei Gerlingen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-gerlingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* | * vorher Bibliotheca | ||
* | * seit Dezember 2021 | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Giessen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.giessen.de/stadtbibliothek Stadtbibliothek Giessen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb- | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-giessen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit | * seit Oktober 2019 | ||
* Unterstützt | * Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Glücksburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadtbuecherei-gluecksburg.de/ Stadtbücherei Glücksburg]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-gluecksburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt | * Seit Mai 2019 | ||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Göttingen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.nw-fva.de/ Nordwestdeutsche Forstliche Versuchsanstalt]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | nur intern | ||
| | |||
* seit April 2022 | |||
* 18'900 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Allegro zu Koha 21.05 | |||
|- | |||
| Goslar | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://stadtbibliothek.goslar.de/ Stadtbibliothek Goslar]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-goslar.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Dezember 2021 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Gotha | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.thueringen.de/th1/tsk/kultur/staatsarchive/standorte/gotha/ Landesarchiv Thüringen - Staatsarchiv Gotha]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://tsago.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Zeile 673: | Zeile 856: | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Greiz | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://landesarchiv.thueringen.de/greiz/ Landesarchiv Thüringen - Staatsarchiv Gotha]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://tsagrz.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt | * Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Grenzach-Wyhlen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.grenzach-wyhlen.de/Gemeindebuecherei Gemeindebücherei Grenzach-Wyhlen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-grenzachwyhlen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* seit | * seit Oktober 2021 | ||
* | * Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Griesheim | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.griesheim.de/bildung-kultur/stadtbuecherei/ Stadtbücherei Griesheim]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-griesheim.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* seit | <!-- | ||
* | * seit November 2020 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Hamburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://thenew.institute/de The New Institute]</span> | ||
| | | nur intern | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit 2022 | ||
* | * Unterstützt durch Effective Webworks | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Hameln | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.hsw-hameln.de/ Hochschule Weserbergland / HSW]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek.hsw-hameln.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | |||
* seit Februar 2023 | |||
* 11'700 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Allegro zu Koha 22.11 | |||
|- | |||
| Hamm | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.hshl.de/ Zentrum für Wissensmanagement, Hochschule Hamm-Lippstadt]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://hshl.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit 2013 | ||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
* Unterstützt | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Hanau-Grossauheim | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://bibliothek-grossauheim.de/ Bibliothek Grossauheim]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | nur intern | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit Mitte 2015 | ||
* 27'000 Medien | |||
* | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Harpstedt | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.harpstedt.de/index.php/einrichtungen/buechereien Samtgemeindebücherei Harpstedt]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sgb-harpstedt.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Seit April 2017 | ||
* Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha | * Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha | ||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | * Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Hattingen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.hattingen.de/stadt_hattingen/Bildung%20und%20Kultur/Stadtbibliothek/ Stadtbibliothek Hattingen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-hattingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* seit Dezember 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Heidelberg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bibliotheca-laureshamensis-digital.de/ Bibliotheca Laureshamensis - digital: Virtuelle Klosterbibliothek Lorsch]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://hs-lorsch.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Ausschliesslich Handschriften | ||
* [https://opus4.kobv.de/opus4-bib-info/frontdoor/index/index/docId/1450 "PalatinaSearch" - Koha macht's möglich] | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Heidelberg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.sintiundroma.de/ Dokumentations- und Kulturzentrum Deutscher Sinti und Roma]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://207.180.240.232/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* seit | * seit Juli 2019 | ||
* | * 13'700 Titeldatensätze | ||
* Migration von | * Migration von Allegro-C zu Koha 18.11 | ||
* | * [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Dokumentations- und Kulturzentrums Deutscher Sinti und Roma mit Koha 18.11|Produktionsbeginn des Dokumentations- und Kulturzentrums Deutscher Sinti und Roma mit Koha 18.11]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Heidelberg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.embl.org/ European Molecular Biology Laboratory]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://libcatalog.embl.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* seit Juli 2021 | |||
* 13'600 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Inmagic Genie zu Koha 20.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des European Molecular Biology Laboratory mit Koha 20.11|Produktionsbeginn des European Molecular Biology Laboratory mit Koha 20.11]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Heidelberg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.hfjs.eu/ Hochschule für Jüdische Studien]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://hfjs.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* War die erste Hochschulbibliothek im deutschsprachigen Raum, welche im Oktober 2009 mit Koha in Betrieb ging - eingesetzt wurde damals Koha 3.2 | |||
* Erste Hochschulbibliothek mit Koha in Deutschland (Oktober 2009) - <span class="plainlink">[http://swop.bsz-bw.de/volltexte/2009/775/pdf/Koha_BSZ_Kolloq09_stabenow_fischer.pdf Präsentation]</span> | |||
* Die Bibliothek besitzt rund 50'000 Medien, Selbstverbucher und Selbstverbuchung mit RFID | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Heidelberg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.theaterberatung-bw.de/ Theater- und Spielberatung Baden-Württemberg e. V.]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek.theaterberatung-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | |||
| | | | ||
* seit Januar 2022 | |||
* 13'000 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von BIB2 zu Koha 21.05 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der Theater- und Spielberatung Baden-Württemberg e. V. mit Koha 21.05|Produktionsbeginn der Theater- und Spielberatung Baden-Württemberg e. V. mit Koha 21.05]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Heidesee | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | Ernst-Thälmann-Bibliothek <!-- <span class="plainlink">[ ]</span> --> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://dkponline-bibliothek.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
http://62.75.209.162/ | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Heilbronn | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.seminare-bw.de/SEMINAR-HEILBRONN-GYM,Lde/Startseite Staatliches Seminar für Didaktik und Lehrerbildung (Grundschulen, Werkrealschulen und Hauptschulen und Gymnasien)]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://seminar-heilbronn.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * Unterstützt vom BSZ | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Heilbronn | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://stadtbibliothek.heilbronn.de/ Stadtbibliothek Heilbronn]</span> | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-heilbronn.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Hennef | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.dwa.de/ Deutsche Vereinigung für Wasserwirtschaft, Abwasser und Abfall e. V.]</span> | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[http://litdb.dwa.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* seit | * seit Januar 2020 | ||
* | * 58'700 Titeldatensätze | ||
* Migration von | * Migration von Lotus Notes zu Koha 19.05 | ||
* | * [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der Deutschen Vereinigung für Wasserwirtschaft, Abwasser und Abfall e. V. mit Koha 19.05|Produktionsbeginn der Deutschen Vereinigung für Wasserwirtschaft, Abwasser und Abfall e. V. mit Koha 19.05]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Hennef | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www. | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.hennef.de/index.php?id=430 Stadtbibliothek Hennef]</span> | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-hennef.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Henstedt-Ulzburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.henstedt-ulzburg.de/gemeindebuecherei-mediothek.html Gemeindebücherei Henstedt-Ulzburg]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-henulz.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt | * seit Juni 2019 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Heusenstamm | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.heusenstamm.de/de/freizeit-und-kultur/kulturangebote/stadtbuecherei Stadtbücherei Heusenstamm]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-heusenstamm.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Oktober 2019 | ||
* Unterstützt | * Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Hildesheim | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.hildesheim.de/stadtbibliothek.html Stadtbibliothek Hildesheim]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-hildesheim.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit September 2020 | ||
* Unterstützt | * Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Holzkirchen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.gemeindebuecherei-holzkirchen.de/aktuelles.html Gemeindebücherei Holzkirchen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-holzkirchen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit August 2019 | ||
* | * vorher mit Bibliotheca | ||
* Unterstützt | * Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | ||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Hoyerswerda | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bibliothek-hy.de/ Brigitte-Reimann Bibliothek Hoyerswerda]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-hoyerswerda.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* Unterstützt | * seit Oktober 2019 | ||
* vorher mit Bibliotheca | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Husum | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadtbibliothek-husum.de/ Stadtbibliothek Husum]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-husum.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit Juli 2022 | ||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Ilvesheim | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ilvesheim.de/index.php?id=117 Gemeindebücherei Ilvesheim]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-ilvesheim.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juli 2021 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Ingolstadt | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ingolstadt.de/Kultur/Bildung-Wissenschaft/Stadtb%C3%BCcherei Stadtbücherei Ingolstadt]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-ingolstadt.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* | * seit April 2020 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Ismaning | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.iunworld.com/dienstleistungen/bibliothek/ IUN World GmbH]</span> | ||
| | | nur intern | ||
| | | | ||
* seit | * seit Februar 2020 | ||
* | * 8'000 Titeldatensätze, vier Zweigstellen (Ismaning, Berlin, Unna, Seekirchen) | ||
* Migration von | * Migration von SHSoft BIB2 zu Koha 19.11 | ||
* | * [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der IUN World GmbH mit Koha 19.11|Produktionsbeginn der IUN World GmbH mit Koha 19.11]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Jena | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.abbe-institut.de/ Abbe-Institut für Stiftungswesen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://ais.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* Gefunden Oktober 2021 | |||
* ThüLB Jena | |||
--> | |||
! | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Jena | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://deutsches-optisches-museum.de/ Deutsches Optisches Museum]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://dom.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* | * ThüLB Jena | ||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Jena | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://japs-jena.de/ Jugend-, Aktions- und Projektwerkstatt Jena / JAPS Jena]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://bibo.hacked.jp/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Jena | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://startseite.jena.de/ Stadtverwaltung Jena]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://svj.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* | <!-- | ||
* ThüLB Jena | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Karlsruhe | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ekiba.de/html/content/landeskirchliche_bibliothek.html Landeskirchliche Bibliothek]</span> | |||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://ekiba-lkbib.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* BSZ | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Kemnath in der Oberpfalz | ||
| | | <span class="plainlink">[https://kemnath.de/buergerservice/einrichtungen/stadtbuecherei Stadtbücherei Kemnath]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-kemnath.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
http:// | * seit Juli 2021 | ||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Kiel | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.ipn.uni-kiel.de/de Leibniz-Institut für die Pädagogik der Naturwissenschaften und Mathematik / IPN]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://koha.ipn.uni-kiel.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Migration von Alephino | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Köln | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.dlr.de/ Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt / DLR]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://dlr-archivkatalog.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* | <!-- | ||
| | * unerstützt vom BSZ | ||
* seit September 2016 | |||
= | * vorher Horizon (SirsiDynix) | ||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Korntal-Münchingen | |||
! | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.korntal-muenchingen.de/,Lde/start/Kultur+und+Bildung/Stadtbuechereien.html Stadtbücherei Korntal-Münchingen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-kornmuen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juli 2018 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Kreuztal | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadtbibliothek-kreuztal.de/ Stadtbibliothek Kreuztal]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-kreuztal.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* | <!-- | ||
* seit Juli 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Kronshagen | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.buecherei-kronshagen.de/ Gemeindebücherei Kronshagen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https:// | | <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-kronshagen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* seit März 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
! | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <b>Verbund</b> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http:// | | <span class="plainlink">[http://www.sachsen.rosalux.de/ Rosa Luxemburg Stiftung Sachsen]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://opac. | * RLS Chemnitz | ||
* RLS Dresden | |||
* RLS Leipzig | |||
* Walter-Janka-Bibliothek Chemnitz | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://opac.rls-sachsen.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Ladenburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ladenburg.de/leben-wohnen/stadtbibliothek/ Stadtbibliothek Ladenburg]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-ladenburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* vorher BIBDIA (Axiell) | |||
* seit August 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Lampertheim | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.lampertheim.de/de/freizeit-kultur/kultur/stadtbuecherei/ Stadtbücherei Lampertheim]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-lampertheim.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* | <!-- | ||
* | * vorher SISIS-Sunrise (OCLC) | ||
| | * seit November 2020 | ||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
<!-- | | Lauenburg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.lauenburg.de/leben/stadt-und-schulbuecherei/ Stadt- und Schulbücherei Lauenburg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-lauenburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- Januar 2019 --> | |||
|- | |||
| Leipzig | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.leibniz-gwzo.de/ Leibniz-Institut für Geschichte und Kultur des östlichen Europa / GWZO]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gwzo.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* BSZ | |||
* | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Leipzig | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.eva.mpg.de/german/service/bibliothek.html Max-Planck-Institut für evolutionäre Anthropologie / MPI EVA]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ OPAC]</span> | | <span class="plainlink">[https://biblio.eva.mpg.de/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- | |||
* entdeckt im Dezember 2018 | |||
* | |||
--> | --> | ||
|- | |||
=== | | Leonberg | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.leonberg.de/Familie-Bildung/Stadtb%C3%BCcherei Stadtbücherei Leonberg]</span> | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | | <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-leonberg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* vorher BIBDIA (Axiell) | |||
* seit August 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Mannheim | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.hdwm.de/ Hochschule der Wirtschaft für Management]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://hdwm.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| March | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.march.de/de/Bildung/Gemeindebuecherei Gemeindebücherei March]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-march.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit September 2018 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Markgröningen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.markgroeningen.de/index.php?id=155 Stadtbücherei Markgröningen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-markgroeningen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juni 2021 | |||
* Migration von BiBer/Axiell zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| <b>Verbund</b> | |||
| Medienverbund in der Oberlausitz | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[https://christian-weise-bibliothek-zittau.de/ Christian Weise Bibliothek Zittau]</span> | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek-loebau.de/ Stadtbibliothek Löbau]</span> | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[https://christian-weise-bibliothek-zittau.de/meine-bibliothek/bibliothek-reichenbach-o-l Bibliothek Reichenbach/O.L.]</span> | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[https://christian-weise-bibliothek-zittau.de/meine-bibliothek/fahrbibliothek Fahrbibliothek Landkreis Görlitz]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://mv-oberlausitz.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit April 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Meinigen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://landesarchiv.thueringen.de/meiningen/ Landesarchiv Thüringen - Staatsarchiv Meiningen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://tsamgn.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Meinigen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.meiningermuseen.de/ Meininger Museen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://memu.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Meldorf | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadt-meldorf.de/leben-in-meldorf/stadtbuecherei/ Stadtbücherei Meldorf]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-meldorf.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juli 2021 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Mölln | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.moelln.de/leben-erleben/kinderbetreuung-bildung/stadtbuecherei Stadtbücherei Mölln]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-moelln.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* vorher BIBDIA (Axiell) | |||
* seit August 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Mühlacker | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://muehlacker.de/stadt/bildung-freizeit/kulturelles-leben/bibliothek.php Stadtbibliothek Mühlacker]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-muehlacker.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Mai 2021 | |||
* Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Müncheberg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.archiv-heilpaedagogik.de/ Internationales Archiv für Heilpädagogik]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://biblio.archivhp.de:8081/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| München | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.hfph.de/ Hochschule für Philosophie / IHS]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://hfph.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Seit Juni 2016 | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
* [https://www.hfph.de/nachrichten/neues-bibliothekssystem-mehr-buch-fuer-alle Neues Bibliothekssystem: Mehr Buch für Alle!] | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| München | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.sinologie.uni-muenchen.de/bibliothek/index.html Institut für Sinologie]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://141.84.155.26/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| München | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.macromedia-fachhochschule.de/ Macromedia Hochschule für Medien und Kommunikation / MHMK]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://macromedia.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Zweigstellen in Berlin, Hamburg, Köln und Stuttgart | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | |||
<!-- | |||
|- | |||
| Nachrodt-Wiblingwerde | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.nachrodt-wiblingwerde.de/city_info/webaccessibility/index.cfm?region_id=447&waid=532&item_id=859801&oldrecord=91347&oldmodul=5&olddesign=0&oldkeyword=0&oldeps=20&oldaz=all&oldcat=0&fsize=1&contrast=0 Gemeindebücherei Nachrodt-Wiblingwerde]</span> | |||
| URL ungültig: http://opac.buecherei-nawi.de/ | |||
| | |||
* Koha wurde nur temporär zur Überbrückung bis zum Umstieg auf Winbiap eingesetzt. | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Naumburg (Saale) | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.nietzsche-dokumentationszentrum-naumburg.de Nietzsche-Dokumentationszentrum / NDZ]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://opac.nietzsche-dokumentationszentrum-naumburg.de OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* C. Caetano Da Rosa hat mich 2021 für Update angefragt | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Neudietendorf | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.medienzentrum-ekm.de/ Medienzentrum der Evangelischen Kirche in Mitteldeutschland / EKM]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://ekmn.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Neu-Isenburg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://neu-isenburg.de/kultur-und-freizeit/stadtbibliothek/ Stadtbibliothek Neu-Isenburg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-neu-isenburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit September 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Neumünster | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://neustadt-hessen.de/freizeit-kultur/stadtbuecherei.html Stadtbücherei Neumünster]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-neumuenster.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Seit März 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Neustadt (Hessen) | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.neumuenster.de/kultur-freizeit/stadtbuecherei/ Stadtbücherei Neustadt (Hessen)]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-neustadt.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Seit September 2021 | |||
* vorher ohne Bibliothekssystem | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Neustadt in Holstein | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadt-neustadt.de/stadtbuecherei Stadtbücherei Neustadt in Holstein]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-neustadt-holst.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Dezember 2021 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Niesky | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek-niesky.de/ Stadtbibliothek Niesky]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-niesky.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Seit März 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Norderstedt | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.norderstedt.de/Bildung-Kultur/Bildung/Stadtb%c3%bccherei Stadtbücherei Norderstedt]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-norderstedt.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* vorher BIBDIA (Axiell) | |||
* seit September 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Nordhausen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.buchenwald.de/105/ KZ-Gedenkstätte Mittelbau-Dora / GMD]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://gmd.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Nortorf | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.amt-nortorfer-land.de/stabue Stadtbücherei Nortorf]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-nortorf.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Nürtingen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadtbuecherei-nuertingen.de/ Stadtbücherei Nürtingen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-nuertingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit August 2022 | |||
* Migration von Biber/Axiell zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Oberwolfach | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.mfo.de/ Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach / MFO]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://mfo.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Oelde | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.oelde.de/page.php?p=1465 Stadtbücherei Oelde]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-oelde.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Dezember 2017 | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Oschatz | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.oschatz-erleben.com/stadtbibliothek/ Stadtbibliothek Oschatz]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-oschatz.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juli 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Ossmannstedt | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://wielandforschung.de/ Wieland-Forschungszentrum]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://wfz.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Pforzheim | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://stadtbibliothek.pforzheim.de/ Stadtbibliothek Pforzheim]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-pforzheim.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Pfungstadt | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.pfungstadt.de/freizeit-tourismus/stadtbibliothek.html Stadtbibliothek Pfungstadt]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-pfungstadt.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Dezember 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Plauen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.vogtlandbibliothek.de/ Vogtlandbibliothek Plauen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://vb-plauen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit September 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Pleidelsheim | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.pleidelsheim.de/buecherei/ Ortsbücherei Pleidelsheim]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-pleidelsheim.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* vorher LIBERO | |||
* seit Mai 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Pliezhausen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.gemeinde-pliezhausen.de/de/Kultur/Mediothek-Bibliothek Mediothek Pliezhausen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://mt-pliezhausen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit August 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Plön | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-ploen.lmscloud.net/www.stadtbuechereiploen.de Stadtbücherei Plön]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-ploen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Plochingen am Neckar | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.plochingen.de/,Lde/start/Tourismus_Kultur/stadtbibliothek.html Stadtbibliothek Plochingen am Neckar]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-plochingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Potsdam | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://bib.telegrafenberg.de/ Bibliothek Wissenschaftspark Albert Einstein]</span> | |||
* Deutsches Geoforschungszentrum / GFZ, Helmholtz-Zentrum Potsdam | |||
* Potsdam-Institut für Klimafolgenforschung / PIK | |||
* Alfred-Wegener-Institut / AWI, Helmholtz-Zentrum für Polar- und Meeresforschung, Forschungsstelle Potsdam | |||
* Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies e. V. / IASS Potsdam | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://cat.telegrafenberg.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit September 2015 | |||
* 80'200 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von SISIS-Sunrise V3.5pl1 zu Koha 3.18 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der Bibliothek Wissenschaftspark Albert Einstein mit Koha 3.18|Produktionsbeginn der Bibliothek Wissenschaftspark Albert Einstein mit Koha 3.18]] | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[https://www.kobv.de/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/GFZ_Koha.pdf Von SISIS zu Koha - Koha-Workshop, 23. Januar 2019, KOBV]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| Radeberg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.radeberg.de/inhalte/radeberg/_inhalt/freizeit_tourismus/bibliothek/bibliothek Stadtbibliothek Radeberg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-radeberg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Vorher Bibliotheca | |||
* seit Mai 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Ravensburg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ravensburg.de/rv/kultur-freizeit-einkaufen/stadtbuecherei/aktuelles.php Stadtbücherei Ravensburg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-ravensburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit April 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Reichshof | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.reichshof.org/rathaus-buerger/schule-sport-und-buecherei/buecherei/index.html Gemeindebücherei Reichshof]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-reichshof.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Rellingen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.rellingen.de/leben-erleben/kultur/buecherei-spielkiste/ Gemeindebücherei und Spielkiste Rellingen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-rellingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit April 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Remseck | |||
| Mediathek | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://mt-remseck.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit November 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan=14 | Rendsburg | |||
| colspan=2 | Büchereizentrale Schleswig-Holstein | |||
| rowspan=14 | | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit August 2017 / Fahrbüchereien 14 und 15 im August 2018 | |||
* Koha wurde um die notwendigen Funktionalitäten zur Unterstützung von Büsserbussen erweitert | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[http://www.fahrbuecherei2.de/index.php Fahrbücherei 2 (Rendsburg, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde)]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f2.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Fahrbücherei 3 (Itzehoe, Kreis Steinburg) | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f3.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Fahrbücherei 5 (Husum, Kreis Nordfriesland) | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f5.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Fahrbücherei 6/7 (Tarp, Kreis Schleswig-Flensburg) | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f6f7.lmscloud.net/index.html OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Fahrbücherei 8 (Eckernförde, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde) | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f8.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Fahrbücherei 9/10 (Preetz, Kreis Plön) | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f9f10.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Fahrbücherei 11 (Bargfeld-Stegen, Kreis Stormarn) | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f11.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Fahrbücherei 12 (Norderstedt, Kreis Segeberg) | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f12.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[http://www.fahrbuecherei13.de/index.php Fahrbücherei 13 (Heide, Kreis Dithmarschen)]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f13.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[http://www.fahrbuecherei14.de/index.php Fahrbücherei 14 (Eutin, Kreis Ostholstein)]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f14.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[http://www.fahrbuecherei15.de/index.php Fahrbücherei 15 (Wahlstedt,Kreis Segeberg)]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bzsh-f15.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[http://bz-sh.de/index.php/buechereien/leihverkehrs-und-ergaenzungsbibliothek Leihverkehrs- und Ergänzungsbibliothek]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[http://www.zk-sh.de/opax/index2.html.S Zentralkatalog]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://zksh.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| Renthendorf | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.brehm-gedenkstaette.com/ Brehm-Gedenkstätte]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bgr.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* wohl seit 2020 | |||
* ThüLB Jena | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Rodgau | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.rodgau.de/Kultur-Freizeit/Stadtb%C3%BCchereien Stadtbücherei Rodgau]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-rodgau.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juni 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Rosenheim | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://stadtbibliothek.rosenheim.de/ Stadtbibliothek Rosenheim]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-rosenheim.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Mai 2021 | |||
* Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Rottenburg am Neckar | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadtbibliothek-rottenburg.de/ Stadtbibliothek Rottenburg am Neckar]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-rottenburg.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit August 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Rottweil | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.rottweil.de/244 Staatliches Seminar für Didaktik und Lehrerbildung (Gymnasien)]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://seminar-rottweil.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Rudolstadt | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.thueringen.de/th1/tsk/kultur/staatsarchive/standorte/rudolstadt/ Landesarchiv Thüringen - Staatsarchiv Rudolstadt]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://hbr.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Rudolstadt | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://historische-bibliothek.rudolstadt.de/ Historische Bibliothek Rudolstadt / HBR]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://tsaru.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Saarbrücken | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.leibniz-inm.de/forschung/servicebereiche/ntnm-bibliothek/ NTNM-Bibliothek]</span><br><small>Gemeinsame Bibliothek für Naturwissenschaft und Technik der Naturwissenschaftlich-Technischen Fakultät / NT der Universität des Saarlandes sowie des Leibniz-Instituts für Neue Materialien / INM</small> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://inm.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Ende 2012 | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Saarbrücken | |||
| Ministerium für Bildung und Kultur, Schulbibliotheken | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://schulbib.saarland.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Mai 2019 | |||
* 21'200 Titeldatensätze, 13 Zweigstellen (in Bexbach, Blieskastel, Homburg, Lebach, Merzig, Neunkirchen, Saarbrücken und St. Ingbert) | |||
* Migration von Koha 16.11 zu Koha 18.11 mit neuem Rechner | |||
|- | |||
| Schlitz | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.schlitz.de/leben-wohnen/kultur/buechereien/buecherei-schlitz/ Stadtbücherei Schlitz]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-schlitz.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit November 2021 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Schönkirchen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.buecherei-schoenkirchen.de/ Gemeindebücherei Schönkirchen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-schoenkirchen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juli 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Schotten | |||
| Stadtbibliothek Schotten | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-schotten.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Vorher LIBERO | |||
* seit Juli 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Schwaikheim | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.schwaikheim.de/index.php?id=141 Gemeindebücherei Schwaikheim]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-schwaikheim.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit August 2018 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Schwentinental | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.schwentinental.de/wohnen/buecherei Stadtbücherei Schwentinental]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-schwentinental.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Seit April 2021 | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Sindelfingen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.maichingen.de/,Lde/start/Bildung+und+Leben/Buecherei+Maichingen.html Bücherei Maichingen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://online.buecherei-maichingen.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Zweigstelle der Stadtbibliothek Sindelfingen | |||
* seit September 2016 | |||
* Migration durch Tobias Reimann | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Sondershausen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.sbz-kyffhaeuserkreis.de/joomla/ Staatliches Berufsschulzentrum Kyffhäuserkreis / SBZ Kyffhäuserkreis]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sbzkyf.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Stockelsdorf | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.buecherei-stockelsdorf.de/ Gemeindebücherei Stockelsdorf]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-stockelsdorf.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit September 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Stuttgart | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.hdhbw.de/ Haus der Heimat des Landes Baden-Württemberg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://hdh.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Januar 2013 | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Stuttgart | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.international-school-stuttgart.de/ International School Stuttgart]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://library.issev.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Zweigstellen in Böblingen, Sindelfingen und Stuttgart | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Stuttgart | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.seminar-stuttgart.de/ Staatliches Seminar für Didaktik und Lehrerbildung (Gymnasien, Sonderschulen)]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://seminar-stuttgart.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | |||
<!-- | |||
|- | |||
| Sulzbach | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.thg-sulzbach.de/ Theodor-Heuss-Gymnasium Sulzbach]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://koha.adminkuhn.ch:3000/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* Kostenloses Hosting durch Admin Kuhn | |||
* Datenmigration durch Dennis Burgard | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Sulzfeld | |||
| Gemeindebüchreie Sulzfeld | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-sulzfeld.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Vorher Bibliotheca | |||
* seit Juni 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Tarp | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://buecherei-tarp.de/ Bücherei Tarp]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-tarp.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Taucha | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stadtbibliothek-taucha.de/ Stadtbibliothek Taucha]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-taucha.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit November 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Taunusstein | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.taunusstein.de/info/poi/stadt-und-schulbuecherei-900000006-29880.html Stadt- und Schulbücherei Taunusstein]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-taunusstein.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Telgte | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.buecherei-telgte.de/ Telgter Büchereien]</span> | |||
* Maria-Sibylla-Merian-Gymnasium | |||
* Religio Museum Telgte | |||
* Sekundarschule Telgte | |||
* Stadtbücherei Telgte | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-telgte.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Tornesch | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.buecherei-tornesch.de/ Stadtbücherei Tornesch]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-tornesch.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juli 2021 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Traunstein | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.traunstein.de/kultur-brauchtum/staedtische-kultureinrichtungen/stadtbuecherei/ Stadtbücherei Traunstein]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-traunstein.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit April 2022 | |||
* Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Trebnitz | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://archiv-heilpaedagogik.de/ Internationales Archiv für Heilpädagogik Trebnitz]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://biblio.archivhp.de:8081/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* gefunden Feb. 2021 | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Treuchtlingen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.treuchtlingen.de/Buecherei.82.0.html Stadtbücherei Treuchtlingen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://opac.treuchtlingen.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit September 2015 | |||
* 12'900 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von WinBIAP 4.0.1 zu Koha 3.20 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der Stadtbibliothek Treuchtlingen mit Koha 3.20|Produktionsbeginn der Stadtbibliothek Treuchtlingen mit Koha 3.20]] | |||
|- | |||
| Tübingen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.tuebingen.de/stadtbuecherei/ Stadtbücherei Tübingen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-tuebingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Januar 2019 | |||
* vorher Bibliotheca | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Tuttlingen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.tuttlingen.de/de/Leben-in-Tuttlingen/Bildung/Stadtbibliothek/Stadtbibliothek-Startseite Stadtbibliothek Tuttlingen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-tuttlingen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit September 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Twistringen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.twistringen.de/leben-tourismus/freizeit-kultur/stadtbuecherei/ Stadtbücherei Twistringen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-twistringen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit August 2019 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Uetersen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://uetersen.de/stadtbuecherei.html Stadtbücherei Uetersen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-uetersen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Oktober 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Vallendar | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.whu.edu/fakultaet-forschung/bibliothek/ WHU Otto Beisheim School of Management]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://lms.bib.whu.edu/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit August 2018 | |||
* 51'300 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von SISIS-Sunrise V4.3 zu Koha 17.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der WHU Otto Beisheim School of Management mit Koha 17.11|Produktionsbeginn der WHU Otto Beisheim School of Management mit Koha 17.11]] | |||
|- | |||
| Villingen-Schwenningen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.villingen-schwenningen.de/bildung-soziales/stadtbibliothek/unsere-haeuser/ Stadtbibliothek Villingen-Schwenningen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-villschwenn.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit März 2022 | |||
* Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Warendorf | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.buecherei-warendorf.de/ Öffentliche Büchereien Warendorf]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-warendorf.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Januar 2017 | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Weikersheim | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.weikersheim.de/einrichtungen/stadtbuecherei/ Stadtbücherei Weikersheim]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-weikersheim.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* vorher Bibliotheca | |||
* seit Dezember 2021 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Weimar | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.buchenwald.de/69/ Gedenkstätte Buchenwald]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://gbu.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Weimar | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.stiftung-ettersberg.de/ Stiftung Ettersberg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://ste.thulb.uni-jena.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt von der Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Weingarten | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.seminar-weingarten.de/ Staatliches Seminar für Didaktik und Lehrerbildung (Berufliche Schulen, Gymnasien)]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://seminar-weingarten.bsz-bw.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt vom BSZ | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Wildau | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.wildau.de/public/743968_Bibliothek/ Gemeindebibliothek Wildau]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://koha.wildau.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit April 2012, wohl mit Koha 3.6 | |||
* Unterstützt von der Technischen Hochschule Wildau | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Wuppertal | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.chorverband-ekir.de/ Chorverband der Evangelischen Kirche im Rheinland]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://chorverband.hlb-wuppertal.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Dezember 2015 | |||
* Migration von ComBO 32.037 zu Koha 3.20 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Chorverbands in der Evangelischen Kirche im Rheinland mit Koha 3.20|Produktionsbeginn des Chorverbands in der Evangelischen Kirche im Rheinland mit Koha 3.20]] | |||
|- | |||
| Wyk auf Föhr | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.foehr.de/freizeitangebote/wyk/a-stadtbuecherei-wyk-auf-foehr Stadtbücherei Wyk auf Föhr]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-wyk.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
<!-- | |||
* https://wiki.bsz-bw.de/doku.php?id=l-team:koha:start - BSZ Wiki Koha | |||
** https://wiki.bsz-bw.de/doku.php?id=l-team:koha:koha-handbuch:start - Koha-Anwenderhandbuch | |||
* [http://www.bsz-bw.de/bibliothekssysteme/koha.html Software-as-a-Service] | |||
--> | |||
=== Österreich === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | ! width=10% | Ort | ||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | ! width=45% | Bibliothek | ||
! width=5% | OPAC | ! width=5% | OPAC | ||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | ! width=40% | Bemerkungen | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <b>Verbund</b> | | Dornbirn | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bibliotecanacional.gov.co/content/red-nacional-de-bibliotecas-p%C3%BAblicas Red Nacional de Bibliotecas Públicas]</span> | | <span class="plainlink">[https://stadtbuecherei.dornbirn.at/ Stadtbücherei Dornbirn]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://190.27.214.86/ OPAC]</span> | | <span class="plainlink">[https://katalog.dornbirn.at/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Oktober 2017 | |||
* Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Graz | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.landesbibliothek.steiermark.at/ Steiermärkische Landesbibliothek]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://katalog.landesbibliothek.steiermark.at/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
Steiermärkische Landesbibliothek | |||
Amt der Steiermärkischen Landesregierung - | |||
Abteilung 9 Kultur, Europa, Außenbeziehungen | |||
Joanneumsviertel | |||
Kalchberggasse 2, 8010 Graz | |||
OPAC: https://katalog.landesbibliothek.steiermark.at/ | |||
seit Jänner 2022 online mit 500.000 Titeln | |||
* Migration von Dabis durch HKS3 | |||
* Anreicherung Normdaten | |||
* Plugins | |||
* Onleihe | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Hard | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.buch-hard.at/ Bücherei am Dorfbach]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-hard.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Heiligenkreuz | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://tcmi.edu/resources/about-the-library/ TCM International Institute]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://library.tcmi.edu/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Klosterneuburg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://ist.ac.at/library/ Institute of Science and Technology / IST Austria]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://koha.app.ist.ac.at/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit 2014 | |||
* [https://opus4.kobv.de/opus4-bib-info/frontdoor/index/index/docId/2153 Open Source Bibliothekssysteme als Alternative? Erfahrungen am IST Austria mit Koha] (2015) | |||
* [http://journals.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/index.php/ip/article/viewFile/35227/29619 Ein freies Bibliothekssystem für wissenschaftliche Bibliotheken : Werkstattbericht der IST Austria Library] (2017) | |||
* Unterstützt von Interleaf Technology | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Lustenau | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek.lustenau.at/ Bibliothek Lustenau]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://gb-lustenau.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juni 2022 | |||
* Unterstützung durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Rankweil | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek.rankweil.at/ Bibliothek Rankweil]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sb-rankweil.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Seekirchen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.seekirchen.bvoe.at/ Bibliothek Seekirchen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://oeb-seekirchen.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* vorher Bibliotheca (OCLC) | |||
* seit Oktober 2020 | |||
* Unterstützt von LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Sulz | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.buecherei-sulz-roethis.at/ Bücherei Sulz-Röthis]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://sulz-roethis.lmscloud.net/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Juli 2017 | |||
* Migration von Bibliotheca zu Koha | |||
* Unterstützt durch LMS Cloud | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://a-bibliothek.org/ Anarchistische Bibliothek und Archiv Wien]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://katalog.a-bibliothek.org/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.oefse.at/infoservice/bibliothek/ C3-Bibliothek für Entwicklungspolitik]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://opac.centrum3.at/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Dezember 2019 | |||
* 105'000 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Alephino zu Koha 18.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der C3-Bibliothek für Entwicklungspolitik mit Koha 18.11|Produktionsbeginn der C3-Bibliothek für Entwicklungspolitik mit Koha 18.11]] | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.donjuanarchiv.at/ Don Juan Archiv]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://katalog.donjuanarchiv.at/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Herbst 2014 | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://kdz.eu/ KDZ - Zentrum für Verwaltungsforschung]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://188.40.212.27/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Oktober 2017 | |||
* 16'500 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Aleph Sharing (OBVSG) zu Koha 17.05 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des KDZ Zentrum für Verwaltungsforschung mit Koha 17.05|Produktionsbeginn des KDZ Zentrum für Verwaltungsforschung mit Koha 17.05]] | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.nhm-wien.ac.at/ Naturhistorisches Museum Wien / NHM]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://library.nhm-wien.ac.at/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* vorher ab 1991: MICRO-CDS-ISIS | |||
* Unterstützung durch HKS3 | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.wifo.ac.at/ Österreichisches Institut für Wirtschaftsforschung / WIFO]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://koha.wifo.ac.at/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.ordensgemeinschaften.at/ Ordensgemeinschaften Österreich]</span> | |||
* Bibliothek der Österreichischen Ordenskonferenz | |||
* Erzabtei St. Peter, Salzburg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://cat.telegrafenberg.de/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Mai 2021 | |||
* 166'000 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Aleph zu Koha 20.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der Erzabtei St. Peter mit Koha 20.11|Produktionsbeginn der Erzabtei St. Peter mit Koha 20.11]] | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www2.karmel.at/ Teresianischer Karmel in Österreich]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://bibliothek.karmel.at/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit April 2019 | |||
* 21'100 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Allegro-C und MS Excel zu Koha 18.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Teresianischen Karmels in Österreich mit Koha 18.11|Produktionsbeginn des Teresianischen Karmels in Österreich mit Koha 18.11]] | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://members.aon.at/ukrchurch/deutsch/index.html Ukrainische Griechisch-katholische Zentralpfarre zu St. Barbara]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://library.st-barbara-austria.org/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.unido.org/ United Nations Industrial Development Organization / UNIDO]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.unido.org/cgi-bin/koha/opac-main.pl OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://wiiw.ac.at/ Wiener Institut für Internationale Wirtschaftsvergleiche / WIIW]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://library.wiiw.ac.at/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit 2017 | |||
* Migration von Libero zu Koha | |||
* 13'000 Medien | |||
* Migration durch Mirko Tietgen | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.wienmuseum.at/ Wien Museum]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek.wienmuseum.at/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Mirko Tietgen | |||
* vielleicht 2019? | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Wien | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.zamg.ac.at/ Zentralanstalt für Meteorologie und Geodynamik / ZAMG]</span> | |||
| nur intern | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* seit Mitte 2017 | |||
--> | |||
|} | |||
=== Schweiz === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=45% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=40% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Alpnach Dorf | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.svk.ch/ Schweizerischer Verein für Kältetechnik / SVK]</span> | |||
| nur intern | |||
| | |||
* seit Mai 2017 | |||
* Neueinführung von Koha 16.11 | |||
* Unterstützt durch Admin Kuhn in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Institut für Energiesysteme und Fluid-Engineering an der Zürcher Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Schweizerischen Vereins für Kältetechnik mit Koha 16.11|Produktionsbeginn des Schweizerischen Vereins für Kältetechnik mit Koha 16.11]] | |||
|- | |||
| Baden | |||
| M. Lötscher | |||
| nur intern | |||
<!-- | |||
* Admin Kuhn | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Bern | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bibnet.org/ Bibnet.org : Literaturdatenbank des Gesundheitswesens]</span> | |||
* Berner Fachhochschule - Fachbereich Gesundheit | |||
* Haute école de santé Fribourg - Hochschule für Gesundheit Freiburg | |||
* Bibliothek und Dokumentation von Pro Senectute Schweiz | |||
* Universität Zürich / Weiterbildungszentrum Careum | |||
* Bibliothek GSBS | |||
* Bildungszentrum Gesundheit Münchenstein | |||
* Bildungszentrum Gesundheit und Soziales Chur | |||
* BZGS Berufs- und Weiterbildungszentrum für Gesundheits- und Sozialberufe St. Gallen | |||
* Höhere Fachschule Gesundheit und Soziales Aarau | |||
* Höhere Fachschule Gesundheit Zentralschweiz | |||
* Kantonsspital Winterthur | |||
* Pflegebibliothek Rudolfinerhaus | |||
* Elbe Klinikum Buxtehude | |||
* Zentrum für Ausbildung im Gesundheitswesen Kanton Zürich | |||
* FHS St. Gallen - Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften | |||
* Berner Bildungszentrum Pflege | |||
* Gesundheitlich-Soziale Berufsfachschule und HF Pflege GSBS | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bibnet.org/vufind/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit 2010 | |||
* über 1 Million Datensätze aus über 5'000 Zeitschriften | |||
* mit Discovery-Oberfläche Vufind 2.2.1 | |||
* <span class="plainlink">[http://www.pflegeportal.ch/pflegeportal/pub/bibnet_org_kooperative_Referenzdatenbank_fuer_das_Gesundheitswesen_2098_1.pdf bibnet.org - Kooperative Referenzdatenbank für das Gesundheitswesen]</span> | |||
|- | |||
| Bern | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.living-room.website/ Living Room]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://archiv.living-room.website/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Februar 2022 | |||
* Neueinführung von Koha 21.11 | |||
|- | |||
| Bern | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.schwarzeschweiz.com/archive Schwarze Schweiz Online Archiv / SSOA]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://archiv.schwarzeschweiz.com/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Dezember 2021 | |||
* Neueinführung von Koha 21.11 | |||
|- | |||
| Brugg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.metron.ch/ Metron AG]</span> | |||
| nur intern | |||
| | |||
* seit Juni 2017 | |||
* 8'200 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von FindInfo zu Koha 16.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der Metron AG mit Koha 16.11|Produktionsbeginn der Metron AG mit Koha 16.11]] | |||
|- | |||
| Einsiedeln | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.kloster-einsiedeln.ch/?id=154 Stiftsbibliothek des Klosters Einsiedeln]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek.kloster-einsiedeln.ch/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Dezember 2015 | |||
* 174'000 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von SISIS-Sunrise V4.1pl2 zu Koha 3.20 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der Stiftsbibliothek des Klosters Einsiedeln mit Koha 3.20|Produktionsbeginn der Stiftsbibliothek des Klosters Einsiedeln mit Koha 3.20]] | |||
|- | |||
| Fribourg | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.eunc.edu/de/ Couvent de Fribourg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://catalogue.albib.biblibre.com/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt durch BibLibre | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Genève | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.archivescontestataires.ch Archives contestataires]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://bibliotheque.archivescontestataires.ch:11093/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Koha 19.05.02 | |||
* Marc Vuilleumier | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Genève | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.wipo.int/ World Intellectual Property Organization / WIPO]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.wipo.int/cgi-bin/koha/opac-detail.pl OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Koha 2.2 | |||
* Unterstützt durch PTFS Europe | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Lausanne | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.vd.ch/autorites/departements/dfjc/sesaf/ocosp/contact/centre-osp-lausanne/ Office cantonal d'orientation scolaire et professionnelle / OCOSP]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://ocosp.biblibre.com/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Seit 2006 | |||
* Zweigstellen in Lausanne, Morges, Nyon, Vevey und Yverdon | |||
* Unterstützt durch Biblibre | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Lausanne | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://biblio.hemu-cl.ch/ Bibliothèque du Conservatoire de Lausanne et de la Haute Ecole de Musique Vaud Valais Fribourg / HEMU]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://opacbiblio.hemu-cl.ch/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt durch Biblibre | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Leysin | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.shms.com/ Swiss Hotel Management School]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://lrc-cat.shms.com/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Unterstützt durch Biblibre | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Montreux | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.ritz.edu/en/campus/campus-accommodation/tourism-courses-cesar-ritz-16-51 César Ritz Colleges]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://library.ritz.edu/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Zweigstellen in Brig, Le Bouveret und Luzern | |||
* Unterstützt durch Biblibre | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Payerne | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.gyb.ch/ Gymnase Intercantonal de la Broye / GYB]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://biblio.gyb.ch/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Koha 2.2 | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Rümlingen || <span class="plainlink">[http://www.schulehomburg.ch/ Kreisschule Homburg]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://bibli.schulehomburg.ch/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Sarnen || <span class="plainlink">[http://www.muri-gries.ch/ Benediktinerkollegium Sarnen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://bibliothek.kollegium-sarnen.ch/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- | |||
* Koha 3.12 | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| Schaffhausen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.phsh.ch/de/Dienstleistungen/Didaktisches-Zentrum/ Didaktisches Zentrum der Pädagogischen Hochschule Schaffhausen]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://bibliothek.phsh.ch/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit April 2017 | |||
* 76'000 Titeldatensätze (inkl. E-Books) | |||
* Migration von SISIS-Sunrise V4.1pl2 zu Koha 16.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn der Pädagogischen Hochschule Schaffhausen mit Koha 16.11|Produktionsbeginn der Pädagogischen Hochschule Schaffhausen mit Koha 16.11]] | |||
|- | |||
| Winterthur | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://stadt.winterthur.ch/gemeinde/verwaltung/stadtkanzlei/stadtarchiv Stadtarchiv Winterthur]</span> | |||
| nur intern | |||
| | |||
* seit Februar 2019 | |||
* 12'600 Titeldatensätze | |||
* Migration von Microsoft Excel zu Koha 18.11 | |||
* [[Mitteilungen/Produktionsbeginn des Stadtarchivs Winterthur mit Koha 18.11|Produktionsbeginn des Stadtarchivs Winterthur mit Koha 18.11]] | |||
|- | |||
| Zizers | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.hoehere-fachschule-sozialpaedagogik.ch/ Höhere Fachschule für Sozialpädagogik Zizers]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://bibliothek.hfs-zizers.ch/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* seit Juni 2019 | |||
* Neueinführung von Koha 18.11 | |||
|- | |||
| Zürich | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.dasregenbogenhaus.ch/ Regenbogenhaus Zürich]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://bibliothek-im-regenbogenhaus.ch/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
== Koha-Anwender weltweit == | |||
Für die vielen tausend weiteren Koha-Bibliotheken ausserhalb des deutschsprachigen Raums kann ich hier nur eine mehr oder weniger zufällige Auswahl auflisten. Hier sollen insbesondere die Links zum jeweiligen OPAC einen Eindruck der Gestaltungsmöglichkeiten vermitteln, die allerdings teilweise sehr stark vom Koha-Standard abweichen. | |||
=== Äthiopien === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Addis Ababa | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.aau.edu.et/library/ University Library Addis Ababa University Libraries]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://libcat.aau.edu.et/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
=== Argentinien === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Córdoba | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.unc.edu.ar/ Universidad Nacional de Córdoba]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://blogs.unc.edu.ar/koha/lang/en/catlogosopacs/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* Umstellung 2007-2010 | |||
* Insgesamt 29 Bibliotheken | |||
* [http://blogs.unc.edu.ar/koha/lang/en/2010/05/31/%C2%A1migracion-completamigration-complete/ Migration complete!] (2010) | |||
|} | |||
=== Australien === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Sydney | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.stlukes.nsw.edu.au/ St. Luke's Grammar School]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://learninghub.stlukes.nsw.edu.au/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
=== Bangla Desh === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Dhaka | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bracu.ac.bd/ BRAC University]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://library.bracu.ac.bd:9292/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
=== Frankreich === | |||
In Frankreich gibt es über hundert Bibliotheken mit Koha-Installationen, darunter die Eliteschule École nationale supérieure des mines de Paris mit 400'000 Medien. | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Besançon | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://ista.univ-fcomte.fr/ Institut des Sciences et des Techniques de l'Antiquité / ISTA]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://koha.mom.fr/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* Teilnahme am Verbund CCI Frantiq | |||
|- | |||
| Metz<br>Nancy | |||
| Bibliothèques universitaires | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Strasbourg | |||
| Médiathéque protestante | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
<!-- | |||
http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Koha | |||
https://maps.google.com/maps/ms?ie=UTF8&t=m&source=embed&oe=UTF8&msa=0&msid=205849403483315235667.0004da81935c6a7e7ea53 | |||
--> | |||
=== Griechenland === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Athen | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.ntua.gr/ Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://koha.lib.ntua.gr/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* National Technical University of Athens / NTUA | |||
|} | |||
=== Grossbritannien === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Stafford | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.staffs.ac.uk/ Staffordshire University]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://libcat.staffs.ac.uk/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* Erste britische Universität, die vollständig zu Koha wechselte | |||
|- | |||
| London | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://www.arts.ac.uk/ University of the Arts London]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[https://libsearch.arts.ac.uk/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
=== Indien === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Cochin | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://library.cusat.ac.in/ Cochin University of Science and Technology / CUSAT]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://opac.cusat.ac.in/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
<!-- Irgendwas stimmt hier nicht: OPAC nicht erreichbar - zudem PHP? | |||
|- | |||
| Kozhikode | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.universityofcalicut.info/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=137&Itemid=297 University of Calicut / C. H. Mohammed Koya Library]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://59.165.190.36/library/simple_opac.php OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* Blog: <span class="plainlink">[http://tech4lib.blogspot.in/ Libsys to Koha migration]</span> | |||
A lot of institutional libraries and public libraries in Kerala have already implemented Koha ILS in their libraries.The entire library system of the Cochin University of Science and Technology (CUSAT) comprising its University Library and the Department Libraries have migrated to the Koha platform | |||
--> | |||
|- | |||
| New Delhi | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://dpl.gov.in/ Delhi Public Library / DPL]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.delhipubliclibrary.in/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* Die Bibliothek besitzt rund 1.5 Millionen Titel | |||
* Der OPAC ist gleichzeitig die Homepage | |||
|} | |||
Siehe auch | |||
* [http://nopr.niscair.res.in/bitstream/123456789/15700/1/ALIS%2059%284%29%20223-230.pdf Adoption and user perceptions of Koha library management system in India] (Vimal Kumar V, Jasimudeen S) | |||
<!-- Koha-OPACs gemäss | |||
* http://ir.inflibnet.ac.in:8080/ir/ViewerJS/#../bitstream/1944/1806/1/45.pdf | |||
* Goa University Library | |||
* University of Mysore | |||
* G B Pant University | |||
* JNCASR | |||
* Chitkara | |||
* Azim Premji | |||
* Delhi Public Library | |||
* T N Ambedkar Law University, Bangalore | |||
* Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum | |||
* Institute of Financial Managment Research, Chennai | |||
* Tamil Nadu veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Chennai | |||
* Central University, Kerala | |||
--> | |||
<!-- | |||
=== Kenia === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Nairobi | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[Parliament of Kenya Library]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
Angeblich nutzt die Parliament of Kenya Library das System Koha | |||
* http://lists.katipo.co.nz/public/koha/2010-August/024993.html | |||
* [http://www.parliaments.info/downloads/16%20KOHA%20-%20Presentation.pdf Koha library management system](2006) | |||
--> | |||
=== Kolumbien === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| <b>Verbund</b> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.bibliotecanacional.gov.co/content/red-nacional-de-bibliotecas-p%C3%BAblicas Red Nacional de Bibliotecas Públicas]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://190.27.214.86/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* Das von der Bibliotéca Nacional de Colombia betreute Netzwerk der Öffentlichen Bibliotheken von Kolumbien mit über 130 teilnehmenden Bibliotheken | |||
|} | |||
<!-- | |||
http://www.organizadatos.com/nuestros-servicios/bibliotecas-archivos-y-museos/koha.html | |||
http://www.museodata.com/rembim/ Red Internacional de Bibliotecas de Museos - Catálogo Colectivo [http://rembim.museodata.com/ OPAC] | |||
--> | |||
=== Neuseeland === | |||
{| class=wiki width=100% | |||
! width=10% | Ort | |||
! width=35% | Bibliothek | |||
! width=5% | OPAC | |||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | |||
|- | |||
| Levin | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.library.org.nz/ Horowhenua Library Trust / HLT]</span> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.library.org.nz/ OPAC]</span> | |||
| | |||
* Auftraggeber der ersten Koha-Version | |||
* ab Januar 2000 allererste Koha-Bibliothek weltweit | |||
* unterstützt von Katipo Communications | |||
* [http://journal.code4lib.org/articles/1638 How hard can it be? : developing in Open Source] (Joann Ransom, Chris Cormack, Rosalie Blake) | |||
* Der OPAC ist gleichzeitig die Bibliotheks-Homepage | |||
|- | |||
| <b>Verbund</b> | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.rangitikeilibrary.org.nz/ Rangiteikei Libraries]</span> | |||
* Bulls Public Library | |||
* Marton Public Library | |||
* Taihape Public Library | |||
| <span class="plainlink">[http://www.rangitikeilibrary.org.nz/cgi-bin/koha/opac-main.pl OPAC]</span> | |||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== | === Niederlande === | ||
{| class=wiki width=100% | {| class=wiki width=100% | ||
| Zeile 1'134: | Zeile 2'714: | ||
! width=50% | Bemerkungen | ! width=50% | Bemerkungen | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Amsterdam | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://www.rijksmuseum.nl/ Rijksmuseum]</span> | ||
| <span class="plainlink">[ | | <span class="plainlink">[https://library.rijksmuseum.nl/ OPAC]</span> | ||
| | | | ||
* [https://theartofinformationblog.wordpress.com/2020/01/08/3725/ Nightwatching Koha for 10 years] | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Zeile 1'425: | Zeile 2'993: | ||
{{Weblinks}} | {{Weblinks}} | ||
{{url_wikikohacommunity|Koha_Users_Worldwide|Koha users worldwide|sublink=<ul> | {{url_wikikohacommunity|Koha_Users_Worldwide|Koha users worldwide|sublink=<ul> | ||
<li>[http://wiki.koha-community.org/wiki/KohaUsers/Europe Koha users Europe] - Eine Liste mit etwa | <li>[http://wiki.koha-community.org/wiki/KohaUsers/Europe Koha users Europe] - Eine teilweise veraltete Liste mit etwa 180 Koha-Anwendern in Europa</li> | ||
</ul>}} | </ul>}} | ||
{{url|US|Library Technology|eng| | {{url|US|Library Technology|eng|https://librarytechnology.org/libraries/search.pl?ILS{{=}}Koha|Items where the library automation system used is Koha|Alphabetische Liste und Weltkarte mit 5'162 Koha-Bibliotheken weltweit (Stand: 17. August 2021). Die Weltkarte ist leider unvollständig.|sublink=<ul> | ||
<li>[ | <li>[https://librarytechnology.org/libraries/map.pl?ILS{{=}}Koha Map of libraries: Koha ILS sites]</li> | ||
</ul>}} | </ul>}} | ||
{{url|NZ|Koha Community|eng|http://hea.koha-community.org/|Koha Community statistics|Eine Statistik mit den Daten von über | {{url|NZ|Koha Community|eng|http://hea.koha-community.org/|Koha Community statistics|Eine Statistik mit den Daten von über 14'900 Koha-Bibliotheken weltweit (Stand: 17. August 2021)|icon=http://www.google.com/s2/favicons?domain=hea.koha-community.org|sublink=<ul> | ||
<li>[https://wiki.koha-community.org/wiki/KohaUsageStat_RFC Hea : Koha usage statistics]</li> | <li>[https://wiki.koha-community.org/wiki/KohaUsageStat_RFC Hea : Koha usage statistics]</li> | ||
</ul>}} | </ul>}} | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 28. Mai 2024, 18:01 Uhr
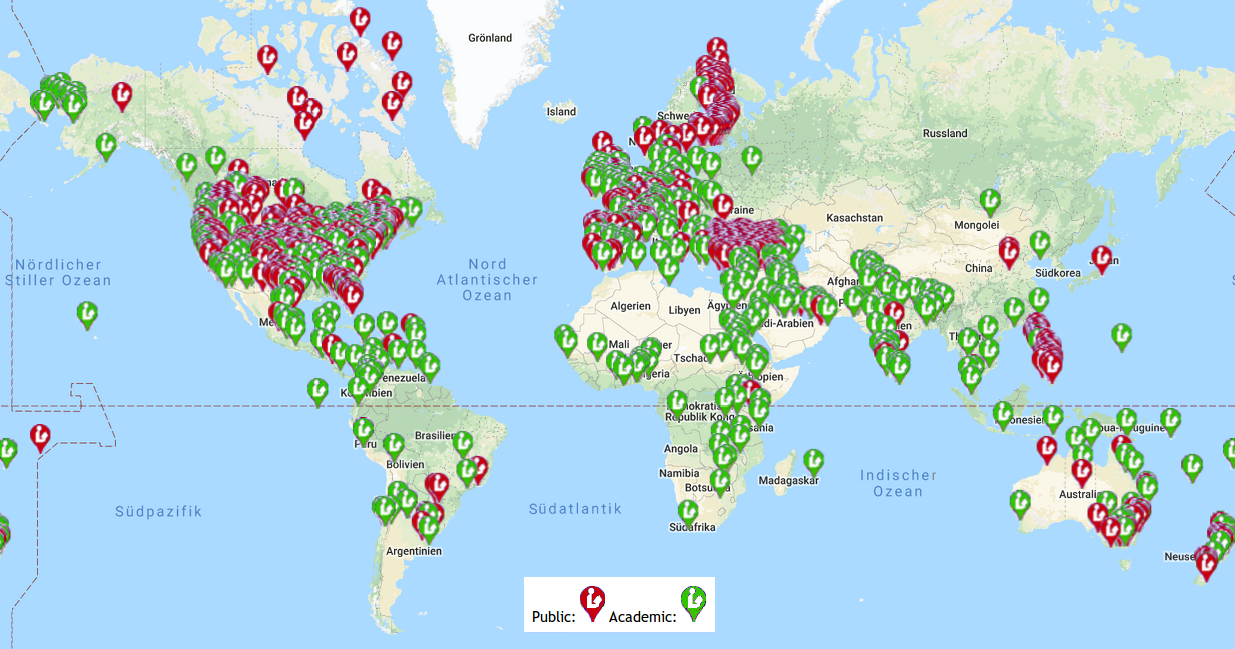
Die Zahl der Anwender des Bibliothekssystems Koha wird auf rund 15'000 Bibliotheken geschätzt. Zu den einsetzenden Bibliotheken gehören solche aller Grössen und Typen - Nationalbibliotheken, öffentliche und wissenschaftliche Bibliotheken sowie Schul-, Firmen- und Spezialbibliotheken.
Viele Anwender von Koha haben sich zu regionalen, nationalen oder sprachabhängigen Koha-Anwendergruppen zusammengeschlossen.
Koha-Anwender weltweit
Zur Zahl der tatsächlichen Koha-Anwender gibt es naturgemäss keine genauen Zahlen, da jeder Beliebige die Software herunterladen und installieren kann, ohne jemanden davon zu benachrichtigen oder dafür bezahlen zu müssen.
Die Firma Catalyst IT sowie der Bibliothekswissenschaftler Marshall Breeding aus den USA schätzten die Zahl der weltweiten Koha-Installation im August 2016 auf rund 15'000. Breeding geht davon aus, dass Koha das weltweit am meisten eingesetzte Bibliothekssystem überhaupt ist. In seinem Bibliotheksverzeichnis libraries.org haben sich davon gegenwärtig 5'989 Bibliotheken freiwillig eingetragen, davon 2'139 aus den USA, 965 aus der Türkei, 472 aus Grossbritannien, 311 aus Frankreich, 70 aus Deutschland, 23 aus der Schweiz und 14 aus Österreich (Stand: 28. Mai 2024).
Galen Charlton beschrieb in seinem Artikel Visualizing the global distribution of Koha installations from Debian packages (August 2016) ein Python-Skript mit dem er die ungefähre geografische Verteilung der Downloads der Koha-Debian-Pakets sichtbar machte. Für die so entstandene Weltkarte verarbeitete er Daten von über 25'000 vollständigen Downloads des Pakets "koha-common" von 9'432 IP-Adressen. Natürlich entspricht nicht jeder Download automatisch einer produktiven Installation. Umgekehrt kommt es aber sicher auch vor, dass zentrale Stellen das Paket nur einmal herunterladen und dann an sehr viel Institutionen verteilen - so gibt es beispielsweise in der Türkei über 900 Bibliotheken mit Koha und dennoch vergleichsweise wenige auf der Karte sichtbare Downloads, womöglich weil die Verteilung dort über das nationale Ministerium für Kultur und Tourismus erfolgt.
Koha-Anwender im deutschsprachigen Raum
Für den deutschsprachigen Raum (Deutschland, Österreich, Schweiz) strebte ich bis Ende 2022 eine vollständige Auflistung an. Seitdem führe ich hier zusätzlich nur noch die durch die Admin Kuhn GmbH migrierten oder betreuten Koha-Anwender auf.
Deutschland
Österreich
Schweiz
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpnach Dorf | Schweizerischer Verein für Kältetechnik / SVK | nur intern |
|
| Baden | M. Lötscher | nur intern | |
| Bern | Bibnet.org : Literaturdatenbank des Gesundheitswesens
|
OPAC |
|
| Bern | Living Room | OPAC |
|
| Bern | Schwarze Schweiz Online Archiv / SSOA | OPAC |
|
| Brugg | Metron AG | nur intern |
|
| Einsiedeln | Stiftsbibliothek des Klosters Einsiedeln | OPAC |
|
| Fribourg | Couvent de Fribourg | OPAC | |
| Genève | Archives contestataires | OPAC | |
| Genève | World Intellectual Property Organization / WIPO | OPAC | |
| Lausanne | Office cantonal d'orientation scolaire et professionnelle / OCOSP | OPAC | |
| Lausanne | Bibliothèque du Conservatoire de Lausanne et de la Haute Ecole de Musique Vaud Valais Fribourg / HEMU | OPAC | |
| Leysin | Swiss Hotel Management School | OPAC | |
| Montreux | César Ritz Colleges | OPAC | |
| Payerne | Gymnase Intercantonal de la Broye / GYB | OPAC | |
| Rümlingen | Kreisschule Homburg | OPAC | |
| Sarnen | Benediktinerkollegium Sarnen | OPAC | |
| Schaffhausen | Didaktisches Zentrum der Pädagogischen Hochschule Schaffhausen | OPAC |
|
| Winterthur | Stadtarchiv Winterthur | nur intern |
|
| Zizers | Höhere Fachschule für Sozialpädagogik Zizers | OPAC |
|
| Zürich | Regenbogenhaus Zürich | OPAC |
Koha-Anwender weltweit
Für die vielen tausend weiteren Koha-Bibliotheken ausserhalb des deutschsprachigen Raums kann ich hier nur eine mehr oder weniger zufällige Auswahl auflisten. Hier sollen insbesondere die Links zum jeweiligen OPAC einen Eindruck der Gestaltungsmöglichkeiten vermitteln, die allerdings teilweise sehr stark vom Koha-Standard abweichen.
Äthiopien
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Addis Ababa | University Library Addis Ababa University Libraries | OPAC |
Argentinien
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Córdoba | Universidad Nacional de Córdoba | OPAC |
|
Australien
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sydney | St. Luke's Grammar School | OPAC |
Bangla Desh
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dhaka | BRAC University | OPAC |
Frankreich
In Frankreich gibt es über hundert Bibliotheken mit Koha-Installationen, darunter die Eliteschule École nationale supérieure des mines de Paris mit 400'000 Medien.
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Besançon | Institut des Sciences et des Techniques de l'Antiquité / ISTA | OPAC |
|
| Metz Nancy |
Bibliothèques universitaires | ||
| Strasbourg | Médiathéque protestante |
Griechenland
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Athen | Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο | OPAC |
|
Grossbritannien
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stafford | Staffordshire University | OPAC |
|
| London | University of the Arts London | OPAC |
Indien
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cochin | Cochin University of Science and Technology / CUSAT | OPAC | |
| New Delhi | Delhi Public Library / DPL | OPAC |
|
Siehe auch
- Adoption and user perceptions of Koha library management system in India (Vimal Kumar V, Jasimudeen S)
Kolumbien
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verbund | Red Nacional de Bibliotecas Públicas | OPAC |
|
Neuseeland
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Levin | Horowhenua Library Trust / HLT | OPAC |
|
| Verbund | Rangiteikei Libraries
|
OPAC |
Niederlande
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amsterdam | Rijksmuseum | OPAC |
Philippinen
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manila | National Library of the Philippines / NLP | OPAC |
|
Ausser der Nationalbibliothek arbeiten auch fast alle öffentlichen Bibliotheken auf den Philippinen mit Koha, zudem einige wissenschaftliche und einige Spezialbibliotheken.
Spanien
Im April 2011 gab ein Mitarbeiter des spanischen Kulturministeriums bekannt, dass dieses eine angepasste Version von Koha unter dem Namen "Kobli" für die Anwendung in den Bibliotheken der spanischen Regierungsbehörden entwickle.
Türkei
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| T.C. Kültür ve Turizm Bakanlığı / Kütüphaneler ve Yayımlar Genel Müdürlüğü | OPAC |
|
USA
California / CA
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Santa Barbara | Antioch University Santa Barbara / AUSB | OPAC |
Massachusetts / MA
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boston | The Boston Conservatory / Albert Alphin Library | OPAC |
|
New Hampshire / NH
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fitzwilliam | Fitzwilliam Town Library | OPAC | |
| Newport | Richards Free Library | OPAC | |
| Sanbornton | Sanbornton Public Library | OPAC | |
| Stratham | Wiggin Memorial Library | OPAC | |
| Troy | Gay Kimball Library | OPAC |
|
| Walpole | Walpole Town Library | OPAC | |
| Verbund | Southern New Hampshire Library Cooperative
|
OPAC |
New York / NY
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brooklyn | Bern Dibner Library of Science and Technology | OPAC |
|
| Orangeburg | Nathan S. Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research Health Sciences Library | OPAC | Health Sciences Library Gateway - von SENYLRC erstelltes (und erweitertes) Web Discovery Portal, bestehend aus Koha kombiniert mit Drupal |
| Poughkeepsie | Vassar Brothers Medical Center Medical Library | OPAC | Info Dispensary - von SENYLRC erstelltes (ursprüngliches) Web Discovery Portal, bestehend aus Koha kombiniert mit Drupal |
Ohio / OH
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verbund | Athens County Public Libraries
|
OPAC |
|
Vermont / VT
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hartland | Hartland Public Library | OPAC |
|
| Plainfield | Goddard College | OPAC |
|
Venezuela
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caracas | Biblioteca Nacional de Venezuela | OPAC |
|
Zypern
| Ort | Bibliothek | OPAC | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nikosia | Near East University / NEU | OPAC |
|
Weblinks
| Herausgeber | Sprache | Webseitentitel | Anmerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| eng | Koha users worldwidewbm
|
Offizielles Wiki | |
| eng | Items where the library automation system used is Kohawbm | Alphabetische Liste und Weltkarte mit 5'162 Koha-Bibliotheken weltweit (Stand: 17. August 2021). Die Weltkarte ist leider unvollständig. | |
| eng | Koha Community statisticswbm | Eine Statistik mit den Daten von über 14'900 Koha-Bibliotheken weltweit (Stand: 17. August 2021) |